Turbochargers vs Superchargers:
Understanding the Difference
Both turbochargers and superchargers are forced induction devices used to increase the power output of an internal combustion engine. However, they differ in their design, functionality, and application.

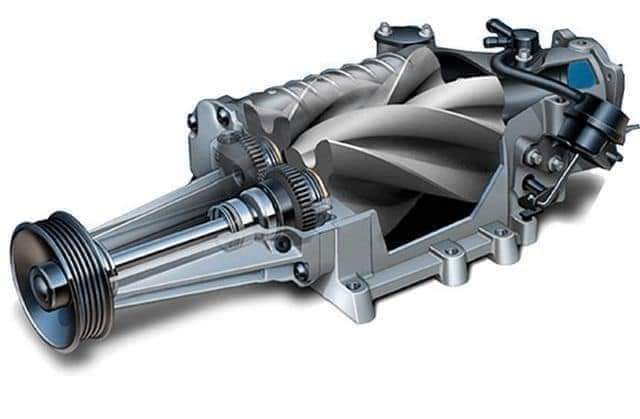
Superchargers
- Mechanical device driven by the engine’s crankshaft
- Uses a belt or chain to compress incoming air and force it into the engine’s combustion chambers
- Provides an immediate boost in power
- Less efficient, as they require engine power to drive them
- Commonly used in applications where immediate power delivery is important, such as:
- Drag racing
- Street applications
- Small engines, where turbo lag is not desirability
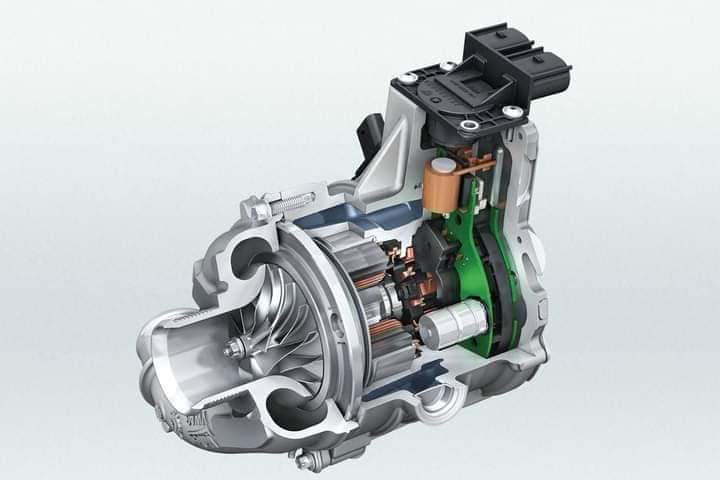

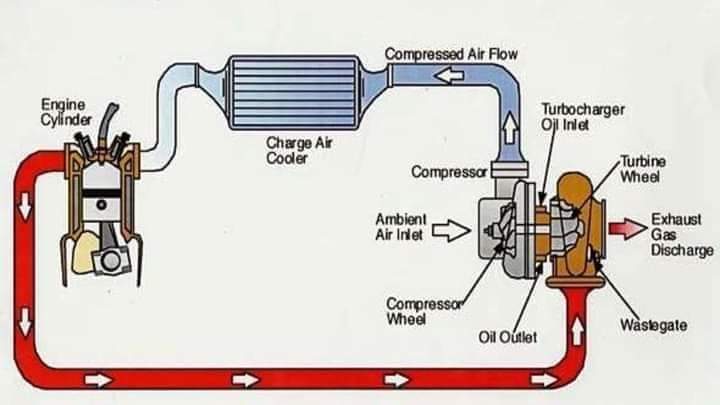
Turbochargers
- Powered by the engine’s exhaust gases
- Consists of a turbine and compressor connected by a shaft
- Exhaust gases spin the turbine, which spins the compressor, compressing incoming air and forcing it into the engine’s combustion chambers
- Requires a moment to spool up before providing significant boost (turbo lag)
- More efficient, as they use waste energy from exhaust gases
- Often used in applications where high power output and efficiency are more important, such as:
- Diesel engines
- High-performance race cars
- Large engines, where turbo lag is less noticeable
Key Differences
- Response time: Superchargers provide immediate boost, while turbochargers require a moment to spool up
- Efficiency: Superchargers are less efficient, while turbochargers are more efficient
- Application: Superchargers are suited for applications where immediate power delivery is important, while turbochargers are suited for applications where high power output and efficiency are more important
Additional Considerations
- Intercooling: Both superchargers and turbochargers can benefit from intercooling, which cools the compressed air before it enters the engine’s combustion chambers, increasing power output and efficiency.
- Boost pressure: The amount of boost pressure provided by a supercharger or turbocharger can significantly impact engine performance and reliability.
- Engine modifications: Installing a supercharger or turbocharger often requires additional engine modifications, such as strengthened engine blocks, crankshafts, and connecting rods.

More Stories
Common Symptoms of a Faulty Crankshaft:
A malfunctioning crankshaft can significantly affect engine performance. The most common symptoms include: Illuminated Check Engine Light:A defective crankshaft sensor...
Diesel vs. Petrol: Which Fuel is Right for You? 🚗⚙️
Choosing between diesel and petrol depends on how you drive. Here's a quick comparison: 🔧 Diesel: ✅ More energy-dense ✅...
understanding your vehicle’s warning and indicator lights:
📖The image displays common car dashboard symbols and their meanings, providing a visual guide to understanding your vehicle's warning and...
Causes and Signs of Damage to the Reverse-Axle Clutch
Graphics The clutch is a critical component in vehicles, consisting of two parts: inner and outer clutch. It transmits power...
Understanding Car Fuses and Fuse Box Symbols
🚗 Graphics 🔧 Ever wondered about the role of fuses in your car? These small yet essential components play a...
Features of the MacPherson Strut Suspension System
Particularly for smaller automobiles, the MacPherson strut is one of the most often used vehicle suspension systems among manufacturers. Drivers...



Average Rating