
Here’s a breakdown of the main engine parts:
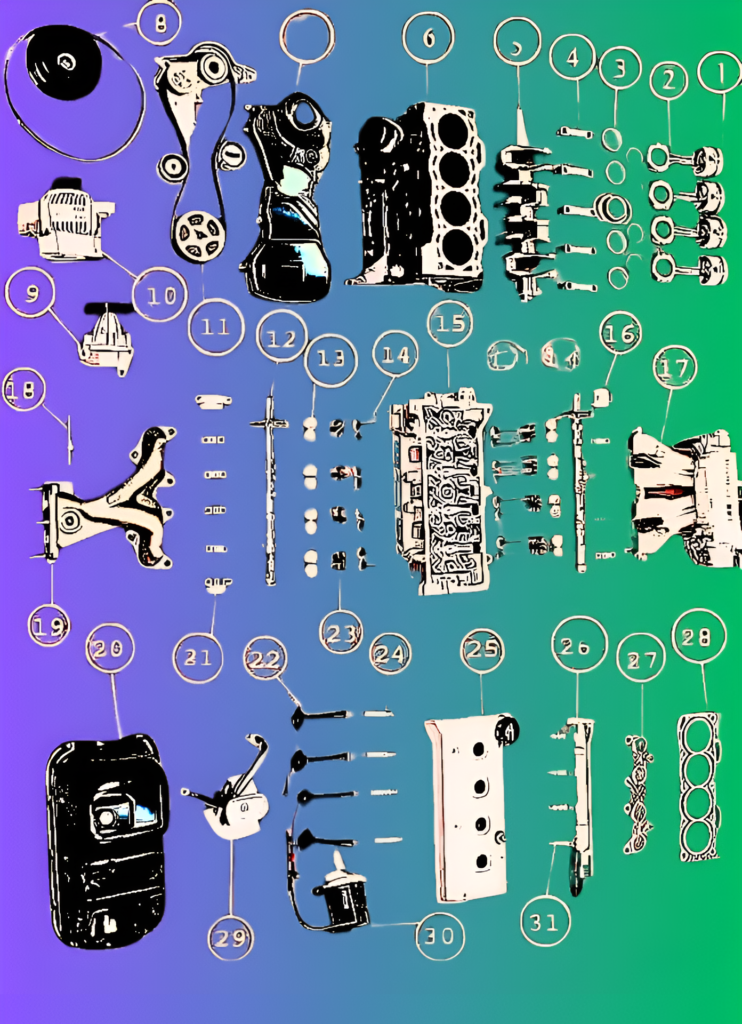
1. Piston: Moves up and down in the cylinder to create power.
2. Connecting Rod: Connects the piston to the crankshaft.
3. Piston Rings: Seal the combustion chamber, control oil, and prevent gas leaks.
4. Crankshaft Bearings: Support the crankshaft and allow it to rotate.
5. Crankshaft: Converts the piston’s linear motion into rotational motion.
6. Cylinder Block: Houses the pistons and crankshaft.
7. Timing Belt Cover: Protects the timing belt from debris.
8. Alternator Belt & Pulley: Drives the alternator to charge the battery.
9. Belt Tensioner: Maintains the tension in the belt system.
10. Alternator: Converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
11. Camshaft Belt, Gear & Pulleys: Controls the timing of the valve opening and closing.
12. Camshaft: Operates the valves in sync with the pistons.
13. Valve Lifters: Transfer motion from the camshaft to the valves.
14. Valves: Control air and fuel flow into the cylinders and exhaust out.
15. Cylinder Head: Sits on top of the cylinder block, housing valves and spark plugs.
16. Camshaft Bearings: Support the camshaft’s movement.
17. Intake Manifold: Delivers the air-fuel mixture to the engine’s cylinders.
18. Temperature Sensor: Monitors engine temperature for efficient operation.
19. Exhaust Manifold: Collects exhaust gases from the engine cylinders.
20. Oil Sump: Stores engine oil.
21. Camshaft Bearings (16): Duplicate part entry, see above.
22. Spark Plug Wires: Transfer electricity to spark plugs for ignition.
23. Valve Springs: Return valves to their closed position.
24. Spark Plugs: Ignite the air-fuel mixture for combustion.
25. Valve Cover: Protects the engine valves and camshaft.
26. Fuel Line: Delivers fuel from the tank to the engine.
27. Exhaust Pipe Gasket: Seals exhaust gases within the system.
28. Cylinder Head Gasket: Seals the cylinder head to the engine block.
29. Oil Pump: Circulates oil to lubricate engine components.
30. Distributor: Distributes electricity to spark plugs in the right sequence.
31. Fuel Injectors: Spray fuel directly into the engine’s intake manifold or cylinders.




Average Rating