Diesel vs Petrol vs Electric vs Hydrogen Car Engines: A Detailed Comparison
📖 Graphics
1. Diesel Engines
Diesel engines are known for their durability, high fuel efficiency, and excellent torque, making them ideal for long-distance driving and heavy-duty vehicles like trucks and buses.
Advantages:
• Fuel Efficiency: Diesel engines typically deliver more miles per gallon (MPG) than petrol engines, making them more cost-effective for long journeys.
• Torque: They offer greater torque at low speeds, ideal for towing and carrying heavy loads.
• Longevity: Diesel engines are generally more robust and last longer than petrol engines due to their design.
Disadvantages:
• Pollution: Diesel engines emit higher levels of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter, contributing to air pollution and health issues.
• Noise: Diesel engines tend to be noisier than petrol or electric engines.
• Cost: Diesel vehicles are often more expensive to buy and maintain, especially with modern emission control technologies like diesel particulate filters (DPFs).
Best For: Long-distance drivers, towing, and heavy-duty applications.
2. Petrol Engines
Petrol (gasoline) engines are the most common and affordable option in many parts of the world. They offer a good balance between power and efficiency, and are suited to a wide range of driving conditions.
Advantages:
• Lower Initial Cost: Petrol cars are generally cheaper to buy than diesel or electric vehicles.
• Quieter Operation: Petrol engines run more smoothly and quietly than diesel engines.
• Widespread Availability: Petrol is readily available worldwide, and petrol stations are abundant.
Disadvantages:
• Lower Fuel Efficiency: Petrol engines consume more fuel than diesel engines, especially at higher speeds.
• Higher CO2 Emissions: Petrol engines emit more carbon dioxide (CO2) than diesel, contributing to climate change.
• Performance Decline: Petrol engines generally wear out faster compared to diesel engines due to higher operating temperatures.
Best For: Urban and suburban drivers looking for affordability and ease of maintenance.
3. Electric Engines
Electric vehicles (EVs) are rapidly growing in popularity due to their zero-emission operation and smooth, quiet driving experience. They rely on electric motors powered by batteries, making them a clean alternative to fossil fuel engines.
Advantages:
• Zero Emissions: Electric engines produce no tailpipe emissions, contributing to cleaner air and reduced greenhouse gases.
• Low Operating Costs: Electricity is generally cheaper than petrol or diesel, and electric motors have fewer moving parts, meaning lower maintenance costs.
• Smooth and Quiet Driving: EVs provide instant torque, smooth acceleration, and a quiet cabin experience.
Disadvantages:
• Limited Range: EVs still have a limited range compared to traditional engines, though this is improving with new battery technologies.
• Charging Infrastructure: Charging stations are not as widespread as petrol stations, and charging times are longer than refueling.
• Battery Degradation: Over time, EV batteries degrade, reducing their range and performance.
Best For: Eco-conscious drivers with access to charging infrastructure, especially for city and suburban use.
4. Hydrogen Engines
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) are an emerging technology that uses hydrogen gas to power an electric motor. They offer the benefits of electric driving with the convenience of quick refueling, similar to petrol and diesel cars.
Advantages:
• Zero Emissions: Hydrogen engines only emit water vapor, making them one of the cleanest vehicle technologies.
• Quick Refueling: Hydrogen cars can be refueled in minutes, much like conventional cars, making them more convenient than EVs with long charging times.
• Long Range: Hydrogen cars typically offer a longer range than battery-electric vehicles, similar to petrol or diesel cars.
Disadvantages:
• Infrastructure: Hydrogen refueling stations are still very limited in most parts of the world.
• Cost: Hydrogen vehicles are expensive to produce and maintain, and hydrogen fuel is costly compared to electricity and even traditional fuels.
• Energy Inefficiency: Producing, storing, and transporting hydrogen requires a lot of energy, which can negate some of its environmental benefits unless renewable energy is used.
Best For: Future-oriented drivers in areas with access to hydrogen refueling infrastructure, looking for a green alternative to conventional fuels.
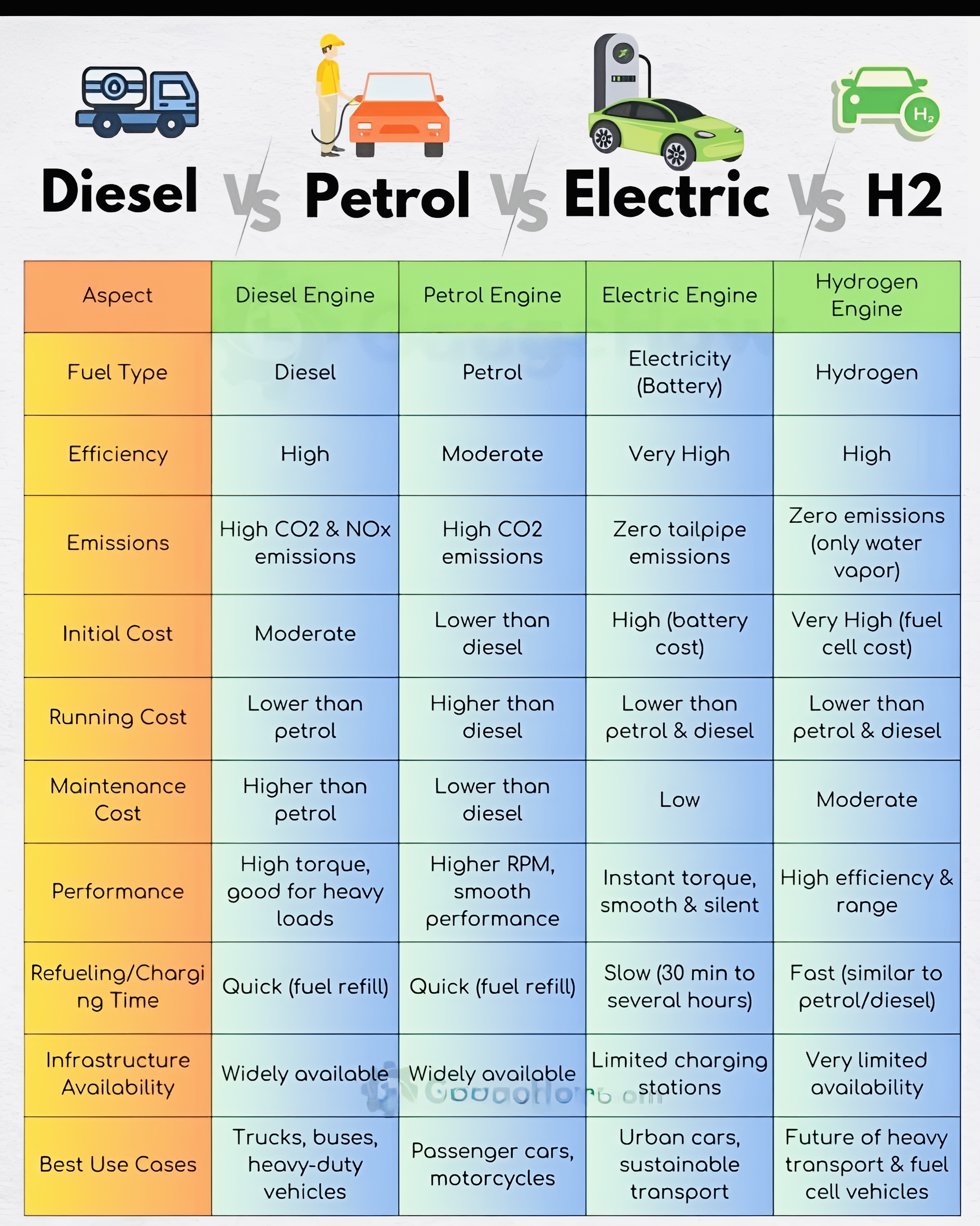
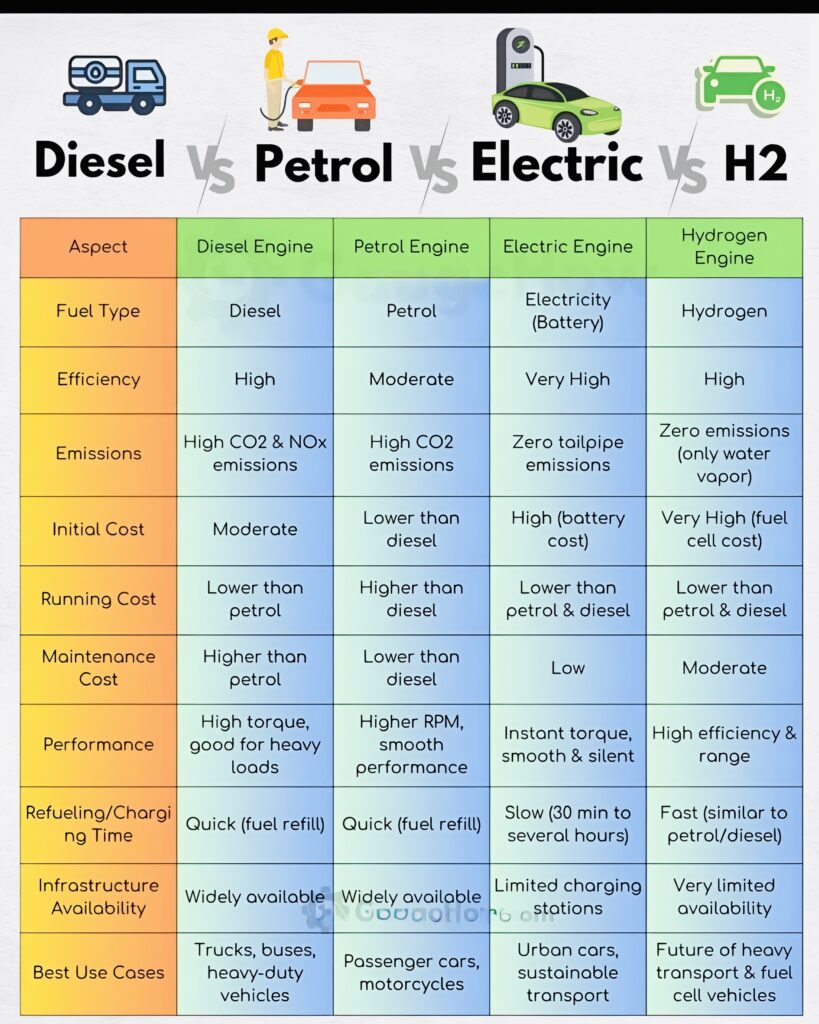
Comparison at a Glance:
Engine Type Fuel Efficiency Pollution Cost Infrastructure Range
Diesel High High (NOx, PM) High upfront Widely available Long
Petrol Moderate High (CO2) Low to moderate Widely available Moderate
Electric Very High (low-cost) Zero High upfront, low operating Limited, growing Limited, improving
Hydrogen High Zero (H2O) Very high Very limited Long
Choosing the Right Engine for You:
• Diesel is great if you need high efficiency for long-distance driving or heavy towing.
• Petrol is a good all-rounder, offering affordability and ease of refueling.
• Electric is the best choice if you’re environmentally conscious and have access to charging points.
• Hydrogen could be the future of clean driving, but it’s still limited by infrastructure and cost.
Each engine type has its pros and cons, and the best option depends on your driving habits, environmental priorities, and budget.
#Automotive #CarComparison #DieselVsPetrol #ElectricVehicles #HydrogenCars #Sustainability #GreenTech #FutureOfCars #VehicleEngines



Average Rating